IELTS Academic Reading: Cambridge 8, Test 4: Reading Passage 3; Collecting Ant Specimens; with top solutions and step-by step detailed explanations
This IELTS Reading post focuses on all the solutions for IELTS Cambridge 8 Test 4 Reading Passage 3, which is entitled ‘Collecting Ant Specimens’. This is an aimed post for IELTS candidates who have great problems in finding answers for the Academic Reading module. This post can guide you the best to comprehend each Reading answer without facing much difficulty. Tracing IELTS Reading answers is a gradual process, and I sincerely hope this post can help you in your IELTS Reading preparation.
IELTS Cambridge 8 Test 4: AC Reading Module
Reading Passage 3:
The headline of the passage: Collecting Ant Specimens
Questions 27-30 (TRUE, FALSE, NOT GIVEN)
In this type of question, candidates are asked to find out whether:
The statement in the question agrees with the information in the passage – TRUE
The statement in the question contradicts the information in the passage – FALSE
If there is no information on this – NOT GIVEN
[For this type of question, you can divide each statement into three independent pieces and make your way through with the answer.]
Question 27: Taxonomic research involves comparing members of one group of ants.
Keywords for this question: Taxonomic research, comparing members, one group of ants,
In paragraph 1, the writer says in lines 4-6, “For taxonomy, or classification, long series, from a single nest, which contain all castes (workers, including majors and minors, and, if present, queens and males) are desirable, to allow the determination of variation within species.”
These lines explain that taxonomic research entails classifying different ants from a particular nest, which holds all the different castes, or different members of a single group.
Here, one group of ants = a single nest, which contain all castes,
So, the answer is: TRUE
Question 28: New species of ant are frequently identified by taxonomists.
Keywords for this question: new species, frequently, identified, by taxonomists,
Only paragraph no. 1 details about taxonomic research of ants. However, no information is found here about how often/frequently taxonomists identify new species of ants.
So, the answer is: NOT GIVEN
Question 29: Range is the key criterion for ecological collections.
Keywords for this question: Range, key criterion, ecological collections,
In paragraph no. 1, the author says in lines 7-8, “For ecological studies, the most important factor is collecting identifiable samples of as many of the different species present as possible.”
The lines suggest that it is absolutely vital/ important to gather a variety or range of present species.
Here, as many of the different species = range, the most important factor = key criterion,
So, the answer is: TRUE
Question 30: A single collection of ants can generally be used for both taxonomic and ecological purposes.
Keywords for this question: single collection, generally, used for, both, taxonomic, ecological purposes,
The last few lines of paragraph no. 1 gives us hint to the answer, “The taxonomist sometimes overlooks whole species in favour of those groups currently under study, while the ecologist often collects only a limited number of specimens of each species, thus reducing their value for taxonomic investigations.”
This means the taxonomists sometimes don’t consider a large collection (whole species) so important while ecologists often collect a very inadequate number of specimens of ever species of ants. This often makes the taxonomic investigation insignificant. Thus, a single collection cannot be used for both taxonomic and ecological purposes.
So, the answer is: FALSE
Questions 31-36 (Classifying statements)
[This type of question asks candidates to classify information from the given reading text. Candidates are given some statements from the text, and a list of options, which are listed as A, B, C, etc. They must match the correct statements with the correct options.
N.B.: This question doesn’t follow any sequence. So, they should be answered after all other questions in the passage.]
Question 31: It is preferable to take specimens from groups of ants.
Keywords for this question: preferable, take specimens, groups of ants,
In paragraph no. 2, where the author talks about hand collecting method, it says in lines 6-8, “. . .. .. when possible, collections should be made from nests or foraging columns and at least 20 to 25 individuals collected. This will ensure that all individuals are from the same species and so increase their value for detailed studies”.
Here, at least 20 to 25 individuals = groups of ants,
So, the answer is: A (hand collecting)
Question 32: It is particularly effective for wet habitats.
Keywords for this question: particularly effective, wet habitats,
The answer can be found in paragraph no. 4, where the writer gives details about ground litter sampling method, “. . .. .. .this method works especially well in rain forests and marshy areas”. Rain forests and marshy areas are wet habitats.
Here, works well = effective, rain forests and marshy area = wet habitats,
So, the answer is: C (sampling ground litter)
Question 33: It is a good method for species which are hard to find.
Keywords for this question: good method, hard to find,
In paragraph no. 3, where the writer details about using baits, it says, “. . . . Baits can be used to attract and concentrate foragers. This often increases the number of individuals collected and attracts species that are otherwise elusive”.
Here, elusive = hard to find,
So, the answer is: B (using bait)
Question 34: Little time and effort is required.
Keywords for this question: little time and effort, required,
In paragraph no. 5, where the author explains the pitfall trap method, it says, “One advantage of pitfall traps is that they can be used to collect over a period of time with minimal maintenance and intervention”.
That means pitfall traps require little time and effort to look after.
Here, minimal maintenance and intervention = little time and effort,
So, the answer is: D (using a pitfall trap)
Question 35: Separate containers are used for individual specimens.
Keywords for this question: separate containers, used, individual specimens,
Again, in paragraph no. 2, where the hand collecting method is explained, the writer says in lines 11-12, “Individual insects are placed in plastic or glass tubes (1.5 – 3.0 ml capacity for small ants, 5-8 ml for larger ants) containing 75% to 95% ethanol.”
Here, plastic or glass tubes = containers,
So, the answer is: A (hand collecting)
Question 36: Non-alcoholic preservative should be used.
Keywords for this question: non-alcoholic preservatives,
In paragraph no. 5, in the pitfall trap method, the writer says, “ . .. . . . .. the preservative used is usually ethylene glycol or propylene glycol, as alcohol will evaporate quickly and the traps will dry out”.
Here, the writer explains the use of ethylene glycol or propylene glycol because if alcohol is used, it will evaporate and the trap will dry out quickly and will not have any effect.
So, the answer is: D (using a pitfall trap)
Questions 37-40 (Labeling a diagram)
[In this type of question, candidates are asked to label a diagram with NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS from the passage. Keywords are important to find answers correctly. Generally, this type of question maintains a sequence. However, we should not be surprised if the sequence is not maintained. Find the keywords in the passage and you are most likely to find the answers.]
Title: One method of collecting ants
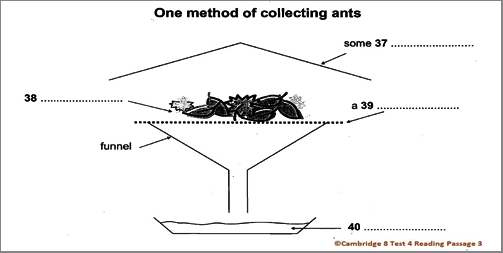
Special tip: To answer this question easily, we need to get an idea about which method of collecting ants is displayed in this diagram and find out the paragraph in the passage where the answers for questions 37-40 can be traced.
In this diagram, we find only one word which seems to be our KEYWORD and the word is ‘funnel’. Therefore, we need to find out the paragraph where the word ‘funnel’ can be found.
This passage has only five paragraphs and paragraphs 2 3, 4 and 5 talk about different methods of collecting the ant specimens.
If we look at paragraph no. 4, we can find the word ‘funnel’ in different lines. So, we can find all the answers in this paragraph.
Question 37: some _________
Question 38: _________
Question 39: a _________
Question 40: some _________
Now, let’s have a close look at paragraph no. 4,
“Many ants are small and forage primarily in the layer of leaves and other debris on the ground. Collecting these species by hand can be difficult. One of the most successful ways to collect them is to gather the leaf litter in which they are foraging and extract the ants from it. This is most commonly done by placing leaf litter on a screen over a large funnel, often under some heat. As the leaf litter dries from above, ants (and other animals) move downward and eventually fall out the bottom and are collected in alcohol placed below the funnel. This method works especially well in rainforests and marshy areas. A method of improving the catch when using a funnel is to sift the leaf litter through a coarse screen before placing it above the funnel. This will concentrate the litter and remove larger leaves and twigs. It will also allow more litter to be sampled when using a limited number of funnels.”
Now, as the picture suggests, the answer to question no. 28 will be leaf litter (they look like leaf and garbage), and as the thing above the leaf litter indicates to question no. 27, the answer will be heat (the heat covers the leaf litter). “This is most commonly done by placing leaf litter on a screen over a large funnel, often under some heat.”(lines 4 and 5)
Then, question no. 39 in the picture shows a covering above the funnel which holds the leaf litter. So, the answer to question no. 39 will be coarse screen. “A method of improving the catch when using a funnel is to sift the leaf litter through a coarse screen before placing it above the funnel.”(lines 7-9)
Finally, for question no. 40, it looks like something below the funnel. So, the answer will be alcohol. “As the leaf litter dries from above, ants (and other animals) move downward and eventually fall out the bottom and are collected in alcohol placed below the funnel.” (lines 5-6)
So, the answers are:
- heat
- leaf litter
- (coarse) screen
- alcohol
Click here for solutions to Cambridge 8 Test 4 Reading Passage 1
Click here for solutions to Cambridge 8 Test 4 Reading Passage 2




hi thank you for your tips and your methods
I am so appriciate
I am Hamideh from Iran
You’re most welcome!